Brand building is a critical part of starting a business. A great business idea or innovative product means nothing if you can’t communicate it to the world—specifically in a way that your target audience can relate to.
Your brand image in the minds of your customers, competition, and the market all comes down to brand positioning and the aesthetic choices you make. But your brand identity is more than a logo. It encompasses everything from your unique brand personality to your mission statement to the consistent color palette you use across every channel. In this guide, learn how to build your own brand from scratch and create a compelling and memorable brand identity that resonates with your target audience. Plus, explore what it takes to create a brand logo or catchy slogan, with real examples from successful brands and branding design tips from experts.
What is a brand?
A brand defines a business, product, service, person, or concept in the market. It differentiates your business from others in the same industry and has a set of rules (called brand guidelines) that dictate how that business will be marketed and presented. Branding is the process of establishing a brand—how it looks, what it sounds like, and the defined target audience it hopes to reach.
What are the building blocks of a brand?
Brand is more than a logo. It’s more than a slogan or colour palette. To build a successful brand, there’s plenty of ground work that needs to be done before you can start designing a website or creating marketing materials.
Here are the building blocks that will be included in your overall brand guidelines document:
Target audience
Defining your target audience is one of the most important stages of creating a brand from scratch. Everything stems from this. Defining your audience in detail helps you build a brand that speaks directly to it. Later in this article, you’ll learn tactics for understanding this audience.
Brand identity
Your brand identity encompasses your business name and the visual elements that define your brand, from your logo and colors to the aesthetic of your photography and your social media handles. Brand identity also includes your brand’s story and competitive advantage.
Brand voice
Brand voice is how your brand sounds. Defining this ensures brand consistency across every customer touchpoint. If your customers expect a cheeky, frank tone from you on social media, carry that through into your website copy and other communications.
Mission and values
Your brand’s mission is the North Star for your business. It establishes both a goal for yourself and a promise to your customers. Your values are what your brand stands for. Both are important as you build your brand because they keep your decisions in check. Whatever you do as a brand should always stay true to your mission and values.
Style guide
Your brand style guide is one part of your larger brand guidelines. It spells out exactly how your brand will surface on every platform or channel. It covers acceptable use of your logo, fonts you use, brand voice and tone, and overall aesthetic of your brand. It’s a useful guide as you scale, hire, and use agencies to create work on your behalf.
The importance of brand guidelines
Brand guidelines are the bible for your brand. This document or set of documents will take a position on every aspect of your brand and how it shows up in various places. Every decision you make during the brand building process will be captured here.
A well-executed set of brand guidelines will achieve the following:
- Keep staff, freelancers, retail partners, and agencies on the same page
- Aid in staff hiring and training (what are the qualities your brand looks for in an employee?)
- Ensure your branding is consistent across all touchpoints
- Be a go-to resource for crisis communications
- Be a flexible document that grows with your brand
How to build a brand in 7 steps
- Research your target market
- Determine your brand’s voice and personality
- Choose your business name
- Write your brand story
- Create a brand style guide
- Design your logo and brand assets
- Apply your branding across your business
As a small business owner, taking the time to establish your brand image is critical, especially if you’re entering a crowded market. And creating a solid foundation for your brand identity can help you build brand awareness over time.
While you might revisit some steps as you pivot or create your brand, it’s important you consider each aspect as you shape your brand identity. Bookmark this guide as a handy resource to access throughout your brand building journey.
1. Research your target market
The first step to building a successful brand is understanding the current market: Who are your potential customers and competitors? Every solid brand strategy and business plan is based on this very question.
You can’t create a brand logo unless you know the preferences of your audience. And developing a unique brand personality that stands out from the crowd can only happen once you know the competitive landscape.
There are many ways to conduct market research before you start the brand building process:
- Google your product or service category and analyze the direct and indirect competitors that appear in search results.
- Talk to people who are part of your target market and ask them what brands they buy from in your industry.
- Look at the relevant social media accounts or pages your target audience follows.
- Shop online or in retail stores and get a feel for how your customers would browse and buy products.
- Investigate trends in your industry by reading publications, browning social media, and using Google Trends.
During your research, take note of the biggest brands in the market. What are they doing right? What do you offer that they don’t? This is called your unique selling proposition (USP).
You should also pay attention to the habits common to your target audience, like the platforms they use most, the language and slang they use, and how they engage with other brands. These insights will help you understand where and how best to reach them.
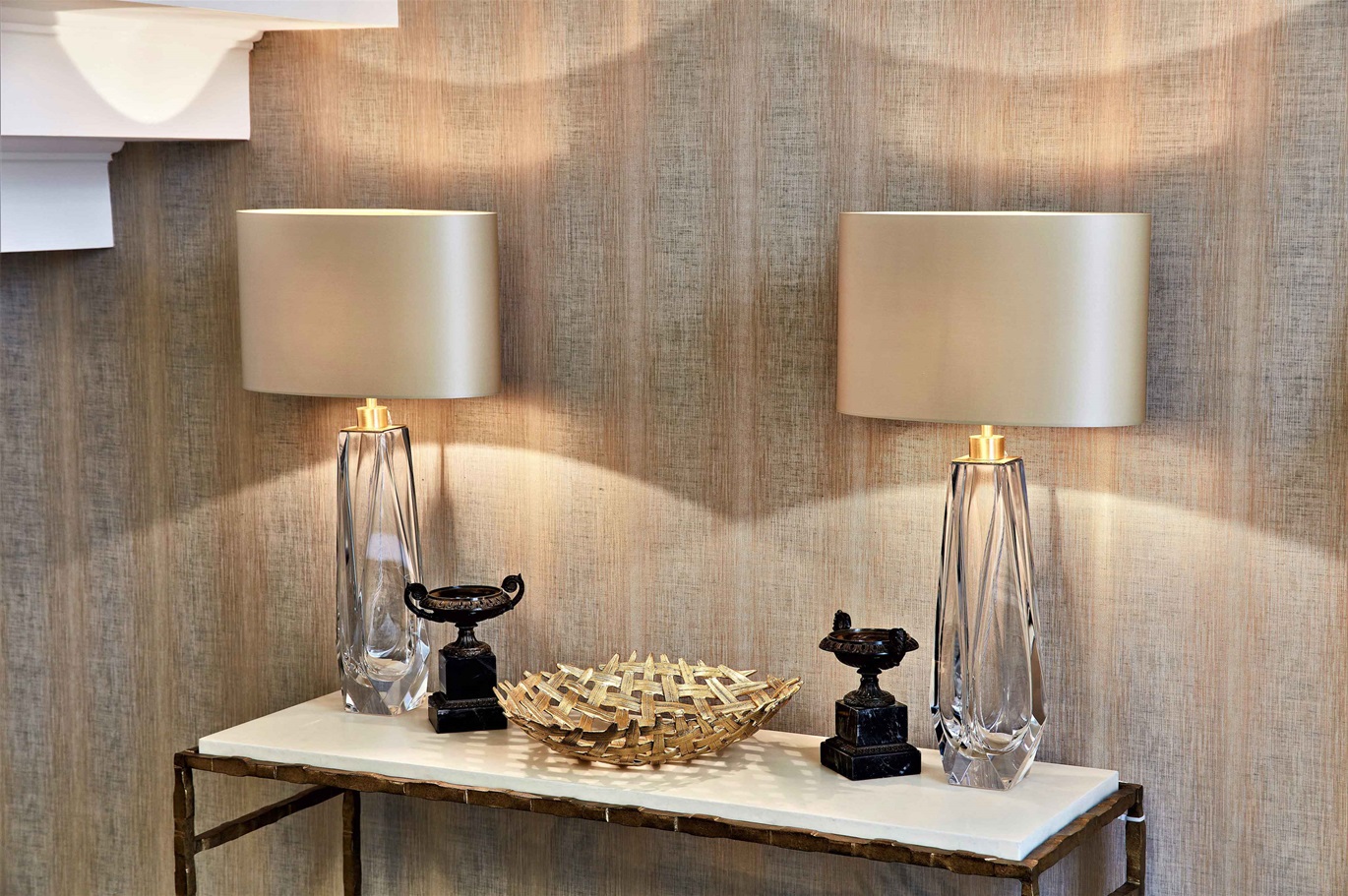
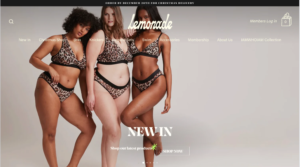
Lingerie brand Lemonade was built to create a size-inclusive and body-positive line of products for “every person.” While this may sound like a broad audience, Lemonade understands that its target customer is someone who doesn’t feel represented by typical lingerie brands.
Beyond saying it, Lemonade shows it’s a brand for all kinds of bodies by using diverse images that include plus models and offering a gender-affirming line.
2. Determine your brand’s voice and personality
Branding isn’t about trying to be everything to everyone. A strong POV will speak to the audience you care about most. It will tell this group that yours is a brand for them. To develop this POV and a distinct brand voice, there are several exercises you can complete.
Create a positioning statement
A positioning statement is one or two lines that stake your brand’s claim in the market. It won’t necessarily be a public-facing statement, but will help steer the direction of your brand story and other parts of your brand guidelines.
A positioning statement should outline what you sell, who it’s for, and what makes you unique. Your value proposition is what’s going to give you an edge—even in a crowded market.
Use this template to create yours:
“We offer [PRODUCT/SERVICE] for [TARGET MARKET] to [VALUE PROPOSITION]. Unlike [THE COMPETITION], we [KEY DIFFERENTIATOR].”
An example positioning statement might look something like this:
“We offer lightweight and waterproof daypacks for travelers, which fold into a wallet-sized pouch when not in use. Unlike other accessory brands, we guarantee our packs for life—no questions asked.”

💡 Tip: You can use this exercise as the basis for your mission statement—expand on your positioning statement to include your brand promise and what you stand for.
Brainstorm using word association
Imagine your brand as a person. What are they like? Do they have the kind of personality your customers would be attracted to? Describe this person. How can your description translate from a person to a brand? Fashion branding expert Joey Ng suggests narrowing your list of adjectives down to just three of the best words. “Find your niche and define in very few words what makes your brand distinctive,” she says. “If something doesn’t fit those original three words—even though you might like it—scrap it. Establish the core message, nail it, then expand.”
Hone your brand voice and tone
Your brand voice and tone will help you hone in on how you want to sound to customers and what you want them to feel when they interact with you. Is your voice cheeky or serious? Does it aim to be a reliable friend, a muse, or a trusted expert?
Establish a list of dos and don’ts that govern the language you will and won’t use in your communications. You may even want to drill down on specific communications channels like social media or customer service: How does your tone change depending on the situation?
3. Choose your business name
Your company’s name is probably one of the first big commitments you’ll make as a business owner. Ideally, you want a brand name that isn’t being used by another company (especially in your industry), has available social media handles, and is a fit based on your brand or products. It should be easy to remember and hard to imitate.
A few approaches to choosing a brand name include the following:
- Make up a brand new word (e.g., Pepsi).
- Reframe a word unrelated to your industry or product (e.g., Apple for computers or Maple for health care).
- Use a suggestive word or metaphor (e.g., Buffer).
- Describe it literally (e.g., The Shoe Company or Home Depot).
- Alter a word by changing its spelling, removing letters, adding letters, or using Latin endings (e.g., Tumblr or Activia).
- Create an acronym from a longer name (e.g., HBO for Home Box Office).
- Use a portmanteau: Pinterest (pin + interest) or Snapple (snappy + apple).
- Use your own name (e.g., Donna Karan or DKNY)
4. Write your brand story
Your brand story is the autobiography of your business and sometimes your own story as a founder. It’s a useful tool for branding because it humanizes your business to create meaningful connections with customers. Buyer trends point to an appetite for meaningful relationships with brands. The best way to do this is through a compelling, transparent, and authentic story.
What elements of your own story will resonate with your target audience? What do they need to know to connect with you as a person? How do you wrap your brand values and mission into your story to tell customers, “This is a brand for you”?
Creating a catchy slogan
Once you’ve established your positioning and your brand story, you can use this work to create a snappy slogan for your business. A good slogan is short, catchy, and makes a strong impression to boost brand awareness.
A clever slogan can increase brand awareness as customers start to recognize it—even when it’s divorced from your brand.
Here are some ways to approach writing your slogan:
- Stake your claim, like this example from Death Wish Coffee: “The World’s Strongest Coffee.”
- Make it a metaphor, just like Red Bull did: “Red Bull gives you wings.”
- Adopt your customers’ attitude, like this unforgettable slogan from Nike: “Just do it.”
- Speak to your target audience, like this example from Cards Against Humanity: “A party game for horrible people.”
- Try a catchy rhyme, like this Folgers coffee slogan: “The best part of waking up is Folgers in your cup.”
- Establish an aesthetic or taste level, like this example from Aritzia: “Everyday luxury to elevate your world.”
5. Create a brand style guide
Now comes the fun part. Your style guide will include all the visual decisions you make for your brand. This guide will come in handy when you build your website, design your social media profile pages, and create product packaging.
Choosing your colors
Colors are important because, alongside copywriting, they tell potential customers how to feel about your brand. While color psychology is a contested science, there are some general associations you can make between color and mood. Moody darker cool colors may complement an edgy brand or a sleep brand while warm pastels tell a soothing story for baby or wellness brands.
Tips for choosing colors for your visual identity:
- Consider how legibly white and black text will appear over your color palette.
- Don’t use too many colors in your logo—it should be identifiable as a single color in a black and white format.
- Research your target market, use focus groups, and understand the specific cultural or demographic differences that might affect a user’s perception of color.
- Limit your palette to one to two main colors, with a set of accent colors that rotate in and out, depending on application.
Selecting a suite of fonts
Fonts work alongside colors to establish a recognizable look for your brand across social, your website, packaging, and other marketing materials.
As a general rule, choose two fonts: one for headings and one for body text (this might not include the font you use in your brand’s wordmark). Home brand Floof uses one sans serif font for navigation and headers and another serif font for the rest of the text. Note that its logo—a simple wordmark of its brand name—is a unique font not used anywhere else:
Save decorative fonts for your logo or in very limited applications while using a simple, accessible font for your website and product information on packaging. Forét’s fonts are simple and clean, making them legible at any size:
Determining aesthetic elements and effects
If you use a lot of lifestyle photography for your brand, you may want to establish a set of rules to set the tone, no matter who’s producing photos. Maybe that includes guidelines for mood, photo filters, colors, or other effects.
You can also design a set of graphic elements that you use across your branded properties. These may be characters, squiggles, or texture effects. Rotten candy brand uses consistent graphic elements like electrified stripes and grainy textures across its branding:
While OffLimits cereal uses a wordmark for its logo, consistent graphic elements like a family of brand mascots show up across all surfaces:
6. Design your logo and brand assets
While a logo design is one of the first things you might think of when building a brand, it should happen later in the process. That’s because it’s a critical identifier for your brand in the wild—and it’s hard to change once you’ve locked it in.
Your logo should be unique, identifiable, and scalable so it works at all sizes. It should also encompass all the work you’ve done on your brand so far. Does it invoke the feeling you hope to inspire in your customers? Does it tell a story that aligns with your brand values? Does it work in your brand colors?
Consider all the places where your brand’s logo will show up:
- Website
- Social media avatar
- Product packaging
- Video ads
- YouTube channel banner
- Browser favicon (the tiny icon that identifies your open browser tabs)
- Email marketing
- Press mentions and partnerships
You may need to create a few versions of your logo to make it work across applications. If you have a text logo, for example, it’ll be almost impossible to read as a favicon or social avatar. Create a simplified visual version of your logo that works as a square or circle.
Types of logos
Wordmarks, lettermarks, and other type-based logos are the most common type of logo for modern brands. But other styles may work better for you, depending on your goals and aesthetic. Some logo types include the following:
- Abstract logos are a combination of shapes and colors that don’t easily tie back to anything in the real world. These are best used as a secondary logo, paired with a wordmark, while you build brand recognition.
- Mascot logos are represented by the face of a character or real person you use as an ambassador for your brand. They can humanize your business by creating a relatable personality. This works best for kids’ brands or those looking for a retro feel (e.g., Wendy’s, Colonel Sanders for KFC).
- Emblem logos are often circular and combine text with an emblem for a luxurious brand design. Avoid making them too fussy or they won’t scale (e.g., Polo Ralph Lauren).
- Icon logos represent your brand as a visual metaphor. Unlike an abstract logo, an icon logo suggests something about the product (e.g., YouTube’s Play button logo).
- Wordmarks or lettermarks are type-based logos that are either your full business name, a combination of letters, or an initial.
Brand identity logo examples
Because of the limitations that exist for each logo type, you can play with a combination of styles as well as have a few secondary logo options. Beauty brand Glossier has a simple wordmark logo used across its website and packaging:
Mushroom-based supplement brand Eons uses a combination of a wordmark and an icons logo (a simplified mushroom shape). These are used together or separate, as you can see here in different applications:

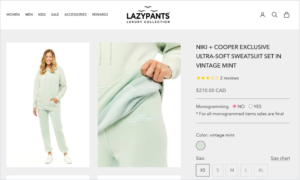
Lazypants also uses this approach, with a combination wordmark and icon that can be used independently, such as in this example where the icon only is stitched into its garments:
Designing your own logo
New brands are often working with a small budget. If this is the case for you, consider designing a logo yourself. You can use a free tool like Canva or try a logo maker. These work by generating sample logos based on basic information about your business.
If you have no design skills or don’t feel confident handling this important task yourself, consider hiring a pro. You can outsource the design through gig sites like Fiverr or Upwork or run a logo contest on 99Designs. If you’re running a business on Shopify, there are many Shopify Experts you can hire to design your brand identity—and even your website.
7. Apply your branding across your business
Applying your branding across your business gives it a cohesive brand story. No matter where customers encounter your brand—through a TikTok ad, in a retail store, or in their inbox—the experience should feel familiar and recognisable. As you build your website, set up your social accounts, and create your marketing plan, refer back to your brand guidelines, mission statement, and values to ensure every decision keeps target customers top of mind. Your website is the palace where you’ll have the most control over your brand identity. Use this space to its fullest potential. eCommerce website templates are a great jumping off point. Most of these, like the themes in Shopify’s Themes Store, are fully customizable, meaning you can apply your brand colors, fonts, and assets to a flexible layout.
Brand building is an evolution
Building a brand doesn’t stop after you design a logo. It is a continuous process of cementing your brand identity in the minds of your customers. Building a successful brand involves being consistent in your messaging and deliberate with your brand marketing. Now that you understand how to build a brand from scratch, you’ll continue brand building for the entire life of your business. You may need to evolve your brand as your values shift or as consumer trends dictate. Remember that if you rebrand, loyal customers should still be able to recognize your brand and receive the same experience. Looping in their feedback will help you grow your brand alongside the people who matter most.


